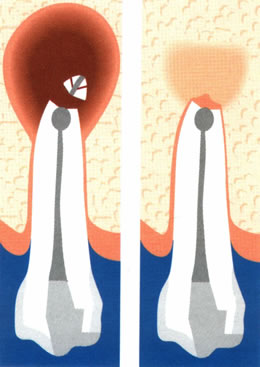
Apicoectomy is a microsurgical procedure performed to remove the tip of a tooth’s root and the infected tissue around it. It is usually recommended when conventional endodontic treatment (root canal therapy) has not fully succeeded in treating the infection or inflammation.