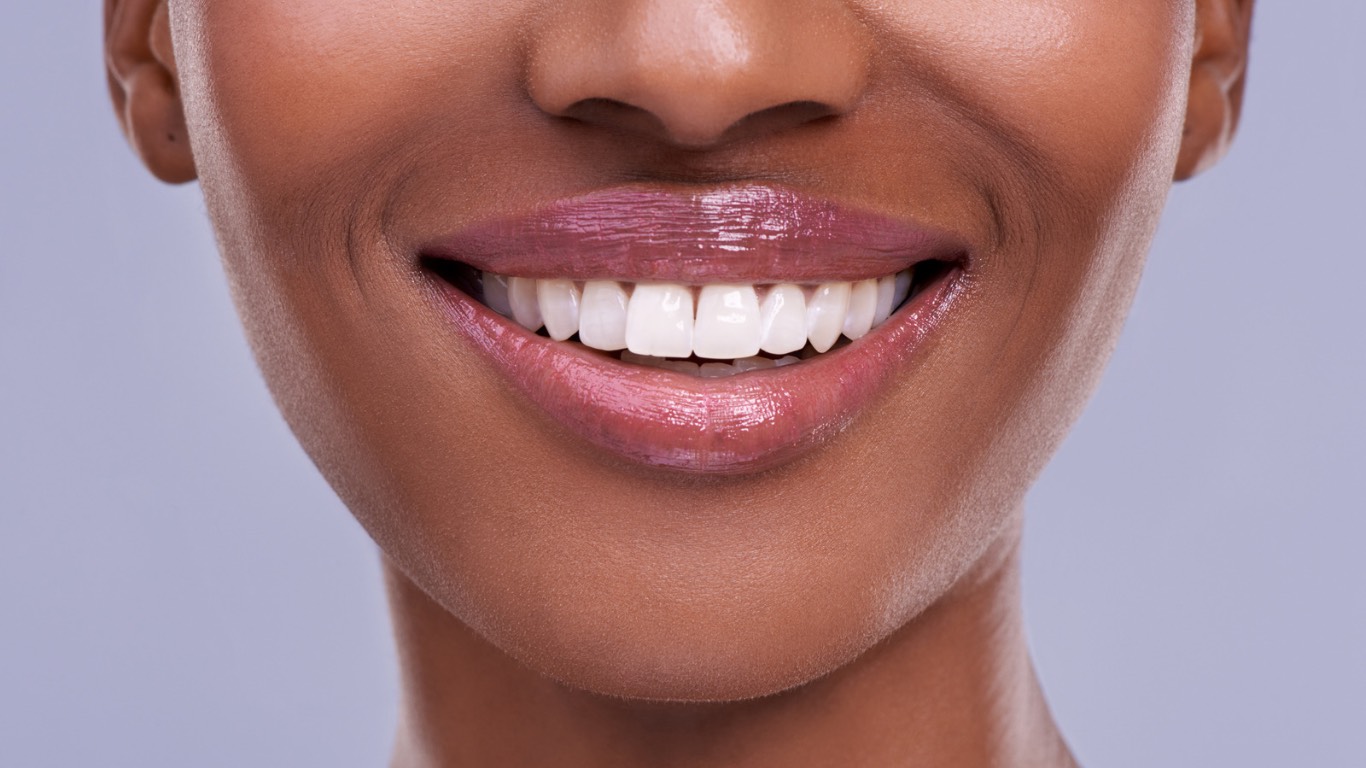
Porcelain veneers are used to correct aesthetic problems such as:
- Tooth discoloration: They can cover discolored teeth that do not respond to whitening treatments.
- Tooth fractures or wear: They can repair teeth with cracks or significant wear that have occurred over time.
- Uneven tooth surfaces: They are used to smooth uneven or irregular surfaces.
- Gaps between teeth: They can close small gaps between teeth and create a harmonious smile overall.
- Tooth irregularities: In some cases, they correct teeth that are tilted or vary in size or shape.
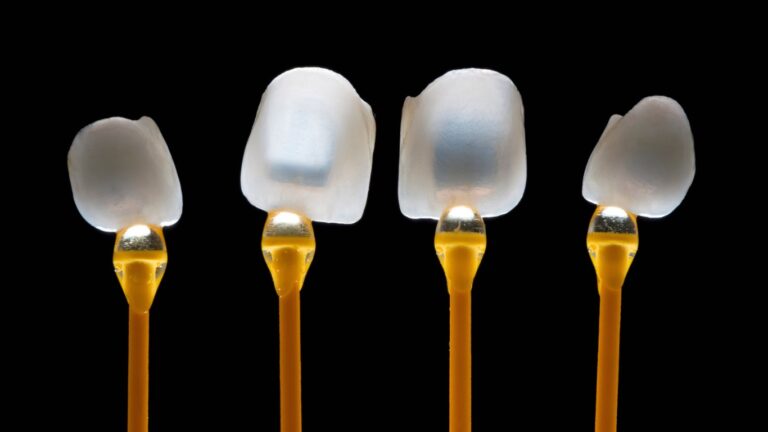
As for the material choice for veneers, it can either be dental porcelain (ceramic material) or composite resin.
However, there are significant differences between these two materials.
Specifically, the choice of ceramic material for veneers is preferred and offers many advantages over other materials such as:
- Natural appearance: Ceramic veneers can mimic the natural color and shine of teeth.
- Durability: They are durable and long-lasting, with a lifespan often exceeding 10-15 years.
- Aesthetic improvement: They provide immediate and noticeable improvement in the appearance of the smile.
However, like any dental procedure, they also come with their own challenges and maintenance requirements. Good oral hygiene and regular visits to the dentist for check-ups and veneer maintenance are recommended.
More specifically, the placement of dental ceramic veneers is a technically demanding procedure that requires specialized knowledge and skill from the dentist. The process involves several critical steps, each of which must be performed accurately to achieve the desired aesthetic and functional outcome.
Steps of the Procedure:
1. Smile Design:
The dentist collaborates with the patient to design the desired smile, considering facial shape, tooth color, and the patient’s personal preferences.
2. Tooth Preparation:
- A thin layer of enamel is removed from the surface of the teeth to create space for the veneers.
- The removal must be precise to ensure the veneers fit perfectly, look natural, and that there is enough space for the veneer material.
3. Taking Impressions:
- Impressions of the teeth are taken to create an accurate model.
- The impression is sent to the dental lab where the veneers are fabricated.
- Temporary veneers may be placed while the permanent ones are being prepared.
4. Veneer Fabrication:
- The veneers are crafted by skilled dental technicians using porcelain or composite resin.
- Precision in fabrication is critical to ensure a perfect fit and a natural appearance.
5. Veneer Placement:
- Before final placement, the veneers are tested on the teeth to confirm proper fit and aesthetics.
- Special adhesives are used to ensure strong and permanent bonding of the veneers to the teeth.
- Placement requires great precision to avoid gaps or imperfections that could cause future problems.
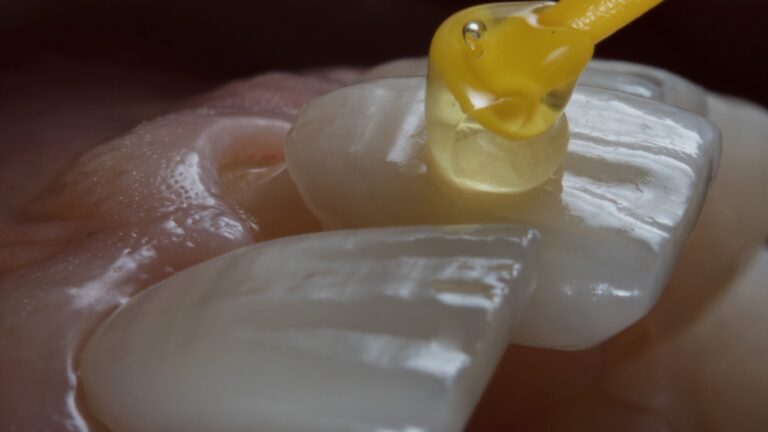

Technical Requirements:
- Precision in Preparation: The dentist must remove exactly the right amount of enamel without causing damage to the teeth.
- Exceptional Skill: The placement of the veneers must be done with millimeter-level accuracy to ensure proper fit and aesthetics.
- Strong Understanding of Materials: The correct choice of material (porcelain or composite resin) and the proper use of adhesives are critical to the success of the procedure.
- Collaboration with Dental Technicians: The dentist must work closely with skilled dental technicians for the fabrication of the veneers.


